 Dr. Alex Hopke joined colleagues from the University of North Carolina School of Medicine
and Emory University as a contributing author for a review article recently published
in the Journal of Leukocyte Biology titled “Multifaceted roles of neutrophils in cardiac
disease.” Cardiovascular disease remains a top contributor to morbidity and mortality
globally. Emerging evidence reveals that neutrophil-driven processes play complex,
impactful roles as mediators of inflammation in a number of chronic conditions, particularly
in cardiovascular diseases. Neutrophils, as key mediators of inflammation, contribute
significantly by both exacerbating tissue damage and contributing to repair processes,
with their role changing in chronic illnesses versus acute disease processes. Dr.
Hopke states, “This review highlights recent discoveries detailing how neutrophils
contribute to the pathogenesis of ischemic heart disease, cardiac arrhythmias, and
nonischemic causes of cardiomyopathy." As scientists increasingly understand the role
of neutrophils, the need for novel treatment strategies clearly are required. New
and ongoing efforts now focus on how selective inhibition of various aspects of neutrophil
function could limit tissue damage and dampen pathogenic remodeling in these chronic
cardiovascular disease states. Current clinical trials in the field investigate therapies
in transcriptional regulation, cytokine inhibition, and cellular recruitment to address
how targeting neutrophils can decrease pathological remodeling to improve clinical
outcomes.
Dr. Alex Hopke joined colleagues from the University of North Carolina School of Medicine
and Emory University as a contributing author for a review article recently published
in the Journal of Leukocyte Biology titled “Multifaceted roles of neutrophils in cardiac
disease.” Cardiovascular disease remains a top contributor to morbidity and mortality
globally. Emerging evidence reveals that neutrophil-driven processes play complex,
impactful roles as mediators of inflammation in a number of chronic conditions, particularly
in cardiovascular diseases. Neutrophils, as key mediators of inflammation, contribute
significantly by both exacerbating tissue damage and contributing to repair processes,
with their role changing in chronic illnesses versus acute disease processes. Dr.
Hopke states, “This review highlights recent discoveries detailing how neutrophils
contribute to the pathogenesis of ischemic heart disease, cardiac arrhythmias, and
nonischemic causes of cardiomyopathy." As scientists increasingly understand the role
of neutrophils, the need for novel treatment strategies clearly are required. New
and ongoing efforts now focus on how selective inhibition of various aspects of neutrophil
function could limit tissue damage and dampen pathogenic remodeling in these chronic
cardiovascular disease states. Current clinical trials in the field investigate therapies
in transcriptional regulation, cytokine inhibition, and cellular recruitment to address
how targeting neutrophils can decrease pathological remodeling to improve clinical
outcomes.
Dr. Alex Hopke is an assistant professor in the Department of Biomedical Sciences where he studies host-pathogen interactions, especially the characterization of the roles and behaviors of neutrophils. He is a CIIDI member.
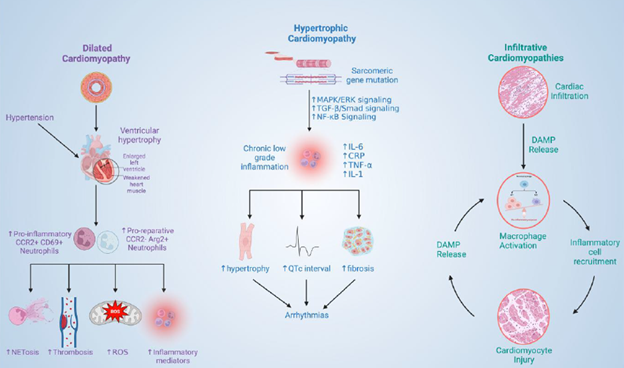
The roles of neutrophils in cardiomyopathy. CRP, C-reactive protein; ERK, extracellular-signal related kinase; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; NF-κB, nuclear factor κB; TGF-β, transforming growth factor β.
 Stout Drive Road Closure
Stout Drive Road Closure