Career Opportunities
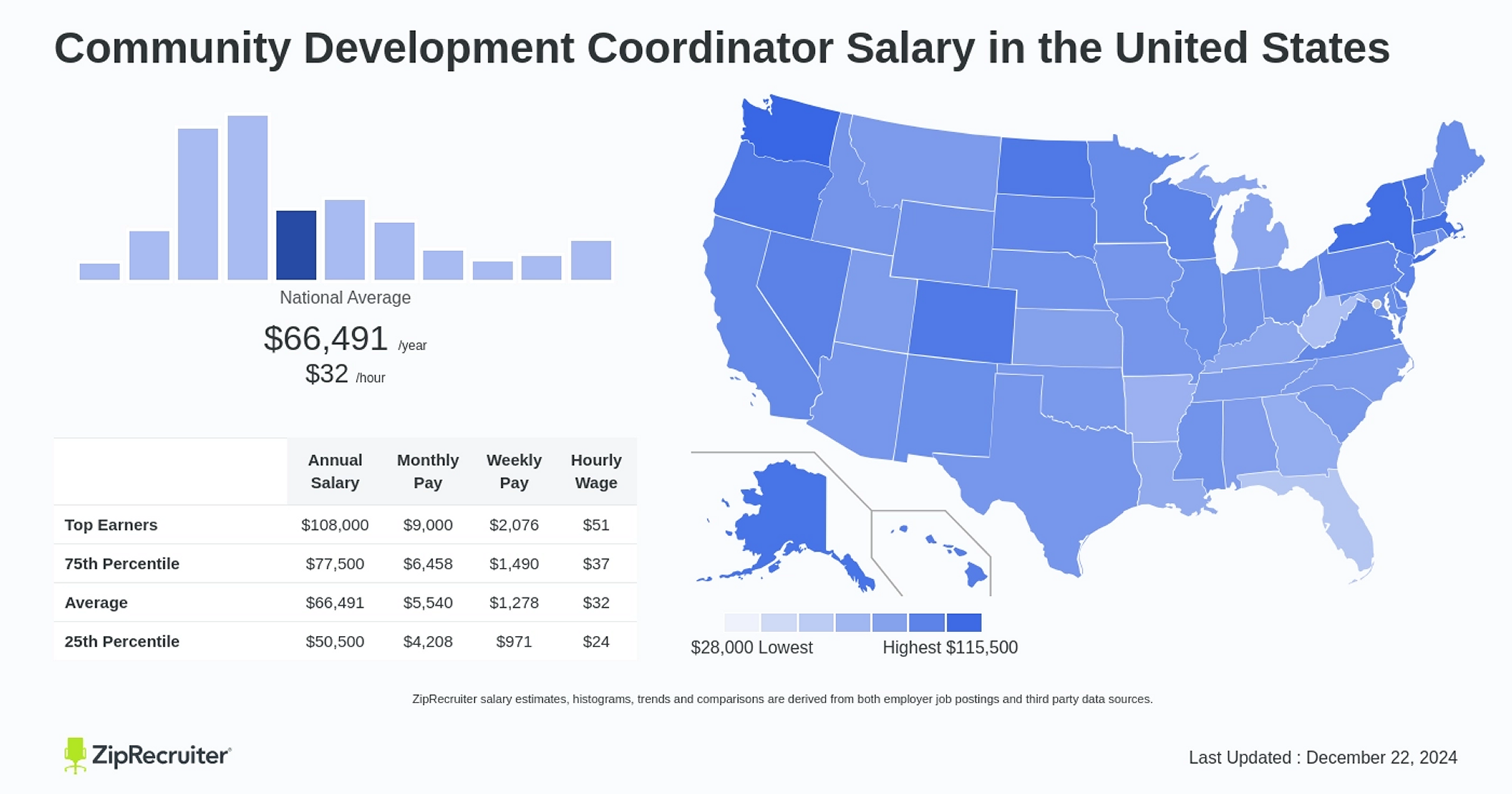
Community Development Coordinator
A Community Development Coordinator plays a crucial role in fostering growth, well-being, and social cohesion within communities. In the context of Appalachian Studies, this role is particularly significant given the unique challenges and opportunities present in the Appalachian region, where social and economic challenges often intersect with unique cultural identities. Community coordinators plan, manage, and implement programs that address a wide array of issues, such as economic inequality, healthcare access, education, infrastructure, and local empowerment.
Community development is not just about improving infrastructure or providing services—it’s about restoring dignity, preserving heritage, and fostering resilience in the face of both historical and contemporary challenges. A Community Development Coordinator plays a central role in ensuring that local communities not only survive but thrive. The work can be challenging and complex, but it also offers the chance to make a meaningful difference in the lives of people who are often overlooked or underserved. Through thoughtful, culturally informed initiatives, a Community Development Coordinator helps communities build a better future while honoring their past.
Role
Work with local governments, nonprofits, or community organizations to develop programs that address issues like poverty, healthcare, education, and infrastructure.
Key Responsibilities
Conducting Needs Assessments: One of the primary first steps in community development is understanding the unique needs of the area. This often requires going beyond surface-level data and engaging with community members to identify their most pressing concerns. This could mean looking at issues like access to healthcare, educational opportunities, economic instability, and social isolation. These assessments usually take a multifaceted approach to understanding the community as well as the issues they are facing and can involve conducting surveys, hosting focus groups, and holding community meetings to get a comprehensive picture of what is required.
Designing and Implementing Programs: Once enough data has been gathered, the Community Development Coordinator creates
specific programs aimed at solving the identified problems. The challenge often lies
in finding ways to implement these programs effectively, ensuring they are culturally
relevant, well-supported, and sustainable over the long term.
Building Partnerships: In most cases, a Community Development Coordinator doesn’t work alone. The role requires
building strong relationships with a variety of stakeholders, from local government
officials and non-profit organizations to private businesses and community leaders.
These partnerships are essential for gaining support, pooling resources, and making
programs more effective. Working with local coalitions, healthcare networks, or educational
institutions help integrate your efforts into the broader regional development framework.
Fundraising and Grant Writing: Most initiatives require financial support, whether through government grants, corporate
sponsorships, or private donations. Securing funding is often one of the most challenging
aspects of community development. A significant part of a coordinators work involves
researching potential funding sources, applying for grants, and organizing fundraising
events. This could range from writing detailed proposals to securing small, community-based
donations, all while ensuring that the funds are used effectively and transparently.
Community Outreach and Advocacy: Effective community development requires ongoing engagement with the people you are
trying to help. Outreach efforts could include hosting community forums, organizing
town halls, or simply attending local events to stay connected with residents. This
outreach helps ensure that the programs you develop are aligned with local needs and
values. In addition, advocacy may be a critical component of your work, particularly
when it comes to lobbying for policy changes or pushing for public investments in
underserved areas. For example, advocating for more equitable healthcare funding or
better transportation infrastructure might be an important part of your role.
Monitoring and Evaluation: After a program has been launched, you would need to assess its effectiveness. This
can involve tracking the number of people reached, collecting feedback from participants,
and measuring the program’s impact on the community. With programs that might need
to address issues like educational attainment or economic mobility, it’s important
to continuously evaluate whether the programs are achieving their goals and to make
adjustments as necessary.
How Appalachian Studies Prepares You for This Role
While Applichian studies focuses on Appalachia’s history, culture, and socio-economic
conditions. Appalachian is a microcosm of nation as whole, and a degree in Appalachian
studies offers an in-depth understanding of events occuring in communities across
the United States.
Cultural Understanding: Appalachian communities are known for their strong sense of identity and deep-rooted traditions. Though homogeneous to outsiders, these communities come from very diffrent social, economic, and ethnic backgrouds. Having an understanding of this cultural fabric is essential when planning and implementing development initiatives. A nuanced understanding of cultural dynamics helps you navigate relationships and build trust with local populations. Being familiar with regional customs, local dialects, and social structures allows you to design programs that feel respectful and in tune with the community.
Awareness of Regional Challenges: Appalachian communities faces a number of issues, including limited access to healthcare,
fewer educational opportunities, and widespread poverty.Though these challenges are
often thought of as unique to the region, they are mirrored in communities accross
the nations. A degree in Appalachian Studies provides you with a detailed understanding
of these issues, which allows you to approach them with both empathy and practical
solutions. The solutions that have been developed in Appalachia have applications
in other regions that are facing simular challenges.
Focus on Social Justice: Appalachian Studies often emphasizes the importance of social justice, particularly as it relates to the region’s marginalized populations. These include communities affected by poverty, poor healthcare, and environmental degradation. Most of the social movements in the united states have their roots in Appalachia, including labor movements, civil rights struggles, and environmental activism. Understanding the history and cultural context of these movements allows a coordinator to make more ethical and practical decisions, ensuring that the community’s needs are addressed in a way that empowers residents and leads to meaningful change.
Environmental Sensitivity: Appalachia’s natural environment—its mountains, forests, and rivers—has always played
a central role in the region’s economy and culture. However, industrial activities
like coal mining have also left significant environmental scars. Appalachian Studies
provides a strong foundation in environmental awareness, which is particularly useful
when addressing the region’s environmental challenges or promoting sustainable development
practices that balance economic and ecological health.
 Stout Drive Road Closure
Stout Drive Road Closure